
| Description :: |
|
One key issue businesses need to address is achieving alignment between business objectives and social objectives. This is absolutely critical as it ensures the success and continuation of business sustainability program. The strategic solutions provide the means of achieving such an alignment. Strategic solutions are “how” a business will achieve its objectives – both business as well as social objectives. Hence, it needs to be examined under both lenses and must meet both sets of requirements.
Strategic objectives define the WHAT? – what needs to be achieved? Whereas strategic solutions define the HOW – how the objectives will be achieved. Crafting strategy necessarily follows objective formulation. It is beyond the purview of this guide to provide guidance on how to craft strategic solutions. Generally, crafting strategic solution requires a sound understanding of the external macro environment (political, social, cultural, legal, technological and economical environment) and internal environment (within the organization). Concerning the external macro environment, the aim is to identify opportunities while taking measures to mitigate threats. Concerning the internal environment, the aim is to identify strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise. For each strategic objective, one or more strategic solutions can be generated. Another important area to consider is performance indicators and results indicators for every strategic solution. It is Performance indicators tell us what we need to do to achieve our target. Generally, performance indicators have a target, data source, threshold and reporting frequency. Performance indicators are leading indicators as they ensure future success. Results indicators report on the result of past performance and hence they are lagging indicators. Leading indicators can be manipulated to enhance and improve performance whereas lagging indicators merely report on the performance after the fact and hence reports information that is too late to act upon. Results indicators reporting frequency is lower than performance indicators. Together these indicators are a powerful combination of performance metrics. Example :: Consider an individual who wants to lose weight. His performance indicator is the number of calories he consumes on a daily basis (measured and reported on a daily basis.). He may set a target of 1800 cal / day (target) and his calorie intake is a direct determinant of future success – weight loss. His actual weight is a result indicator reporting on his past success with the weight loss program.
Constructing a Business Case :: Every strategy a business opts for needs to be justified. This is of utmost importance. A strategy must demonstrate the capacity to generate value and benefits over its cost. A business case is a selling tool to convince the upper management and the executive board to sanction and approve sets of action undertaken in the execution of the strategy. Should it fail to convince the top management, the strategy will be terminated here and now. The Business Case page details out how to construct a convincing business case taking into account not just financial parameters but other parameters as well, thus providing a holistic framework for a sound and accurate analysis. If you have to report to senior management, business case is not an option for you. However, if you are the owner and the sole proprietor, a business case can still assist you in providing a clear picture concerning your strategy. In either case, it is recommended a business case be developed at this stage. |
| Objectives :: |
|
| Methodology :: |
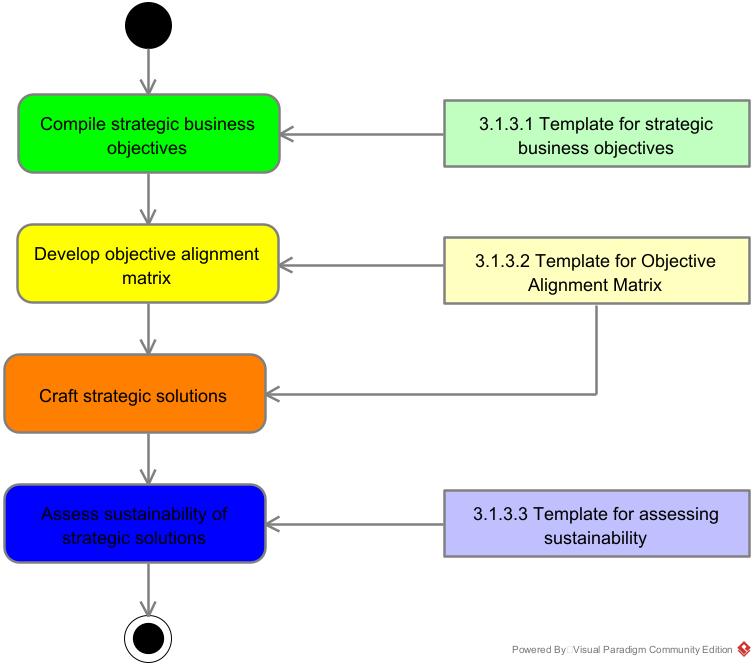 |
| Template 3.1.3.1 | Template 3.1.3.2 |
| Template 3.1.3.3 | |
